Sulfuric Acid
Price 20.0 INR/ Kilograms
Sulfuric Acid Specification
- Melting Point
- Description Sulphuric acid is a strong, corrosive mineral acid widely used in chemical manufacturing, batteries, fertilizers, metal processing, and laboratory applications. It is colorless to slightly yellow, oily, and highly exothermic when mixed with water. Specifications Chemical formula: H SO Molar mass: 98.08 g/mol Appearance: Colorless to yellow, viscous liquid Odor: Odorless Density: ~1.84 g/cm (at 20 C) Boiling point: ~337 C Melting point: 10 C pH: < 1 (very acidic) Concentration grades: 98% (concentrated, industrial grade) 70 80% (battery grade) Hazards: Highly corrosive, causes severe burns, reacts violently with water and organic materials.
- Storage
- Room Temperature
- Form
- Liquid
- Purity
- 99.9%
- Application
- Industrial
Sulfuric Acid Trade Information
- Minimum Order Quantity
- 100 Kilograms
- Delivery Time
- 3 Days
About Sulfuric Acid
Sulphuric acid is a strong, corrosive mineral acid widely used in chemical manufacturing, batteries, fertilizers, metal processing, and laboratory applications. It is colorless to slightly yellow, oily, and highly exothermic when mixed with water.
Specifications
-
Chemical formula: HSO
-
Molar mass: 98.08 g/mol
-
Appearance: Colorless to yellow, viscous liquid
-
Odor: Odorless
-
Density: 1.84 g/cm (at 20C)
-
Boiling point: 337C
-
Melting point: 10C
-
pH: < 1 (very acidic)
-
Concentration grades:
-
98% (concentrated, industrial grade)
-
7080% (battery grade)
-
-
Hazards: Highly corrosive, causes severe burns, reacts violently with water and organic materials.
Industrial Significance of Sulfuric Acid
Sulfuric acid is a cornerstone of industrial chemistry, utilized in producing fertilizers, aiding battery manufacture, and in petroleum refining. Its versatility stems from its strong acidic properties and ability to act as a dehydrating agent. The substance drives core reactions across industries, contributing to enhanced productivity and efficient processing.
Safety Precautions for Storage and Handling
Sulfuric acid should always be stored at room temperature in corrosion-resistant containers. Proper ventilation, use of safety equipment like goggles, gloves, and full-body coverings are essential during handling, as the acid can cause severe burns and reacts violently with water. Emergency protocols must be in place at any facility using sulfuric acid.
FAQs of Sulfuric Acid:
Q: How should sulfuric acid be safely stored and handled in industrial settings?
A: Sulfuric acid must be stored at room temperature in dedicated, corrosion-resistant containers, away from water and organic materials. Proper ventilation and protective gear, including gloves and eye protection, are necessary during handling to prevent exposure to fumes and accidental contact.Q: What applications benefit most from high-purity (99.9%) sulfuric acid?
A: High-purity sulfuric acid is crucial for applications that demand contaminant-free reactions, such as manufacturing electronic components, pharmaceutical synthesis, battery production, and specialized laboratory analyses. Its purity allows for consistent and reliable process outcomes.Q: When is sulfuric acid commonly used in battery manufacturing processes?
A: Sulfuric acid is typically used as the electrolyte in lead-acid batteries, which powers vehicles and backup systems. Its role is essential during both the initial formation and routine operation of batteries due to its high conductivity and reactivity.Q: Where should sulfuric acid be stored within a facility to minimize hazards?
A: Sulfuric acid should be stored in a cool, well-ventilated area, separated from incompatible materials (such as water and organic compounds). The storage area must have spill containment measures, secure access, and should be equipped with emergency eyewash and shower stations.Q: What is the correct process for diluting sulfuric acid for laboratory use?
A: Always add sulfuric acid to water slowly, never the reverse, to avoid violent reactions and splattering. Mixing should be done with constant stirring, in a heat-resistant container, and under a fume hood to mitigate the release of fumes and heat.Q: What are the main benefits of using sulfuric acid in fertilizer production?
A: Sulfuric acid aids in converting phosphate rock into soluble phosphates, which enhance soil fertility. Its use enables the efficient production of fertilizers, vital for sustaining crop yields and agricultural productivity.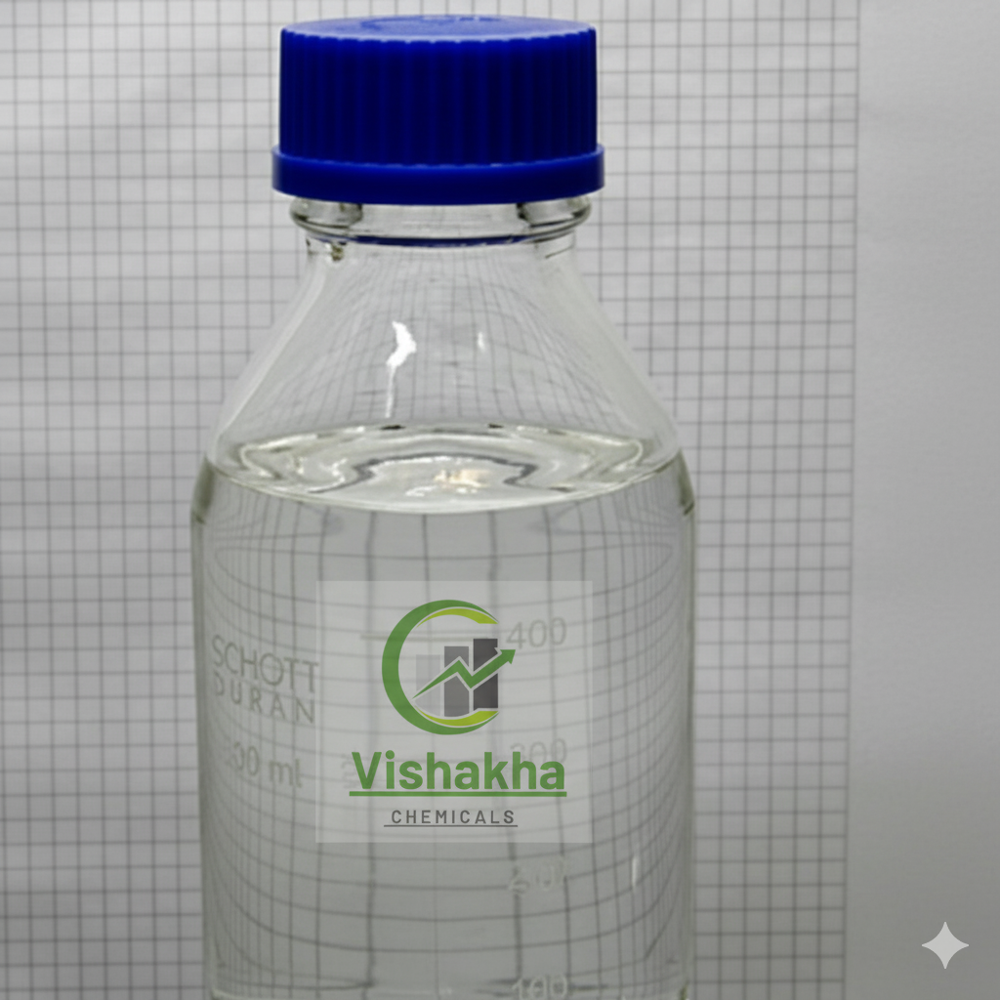

Price:
- 50
- 100
- 200
- 250
- 500
- 1000+
More Products in Liquid Chemical Category
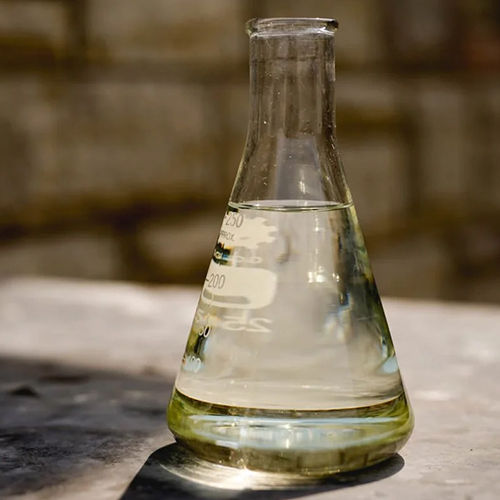
Hydrochloric Acid CP
Price 2 INR / Liter
Minimum Order Quantity : 1000 Liters
Usage : Laboratory
Grade : Other, Lab Grade
Storage : Room Temperature
Purity : 8099%
Sodium Hypochlorite
Price 13.0 INR / Liter
Minimum Order Quantity : 100 Liters
Usage : Laboratory
Grade : Other, Lab Grade
Storage : Room Temperature
Purity : 8099%
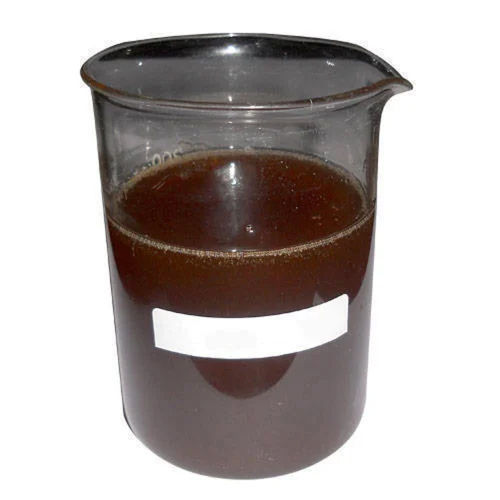
Acid Slurry Labsa
Price 120.0 INR / Liter
Minimum Order Quantity : 100 Liters
Usage : Laboratory
Grade : Other, Lab Grade
Storage : Room Temperature
Purity : 8099%
Liquid Hydrochloric Acid
Price 2.0 INR / Number
Minimum Order Quantity : 1000
Usage : Laboratory
Grade : Other, BioTech Grade
Storage : Room Temperature
Purity : 38%


 Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry





 Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry Send SMS
Send SMS